Orthodontist in
Spokane Valley
*While we do not offer orthodontic care in our office, we frequently collaborate with an orthodontist to design restorative dentistry procedures like dental implants.
Never undervalue the impact of a straight smile! With a gorgeous grin, your self-confidence will soar and you’ll unlock new social and professional doors. You’ll be happy to learn that orthodontic therapy, which may be received at any age, is the original method of enhancing your smile. Nevertheless, it’s not only about appearances: The act of biting, chewing, and even speaking becomes simpler when your teeth are properly positioned. They are also easier to keep clean, which helps prevent tooth decay and gum disease.
Orthodontics is special because it makes use of the body’s innate ability to change its own tissue. Orthodontic appliances gradually alter bone and reposition teeth using gentle, consistent force. These appliances include traditional metal braces, covert clear or tooth-colored braces, and the more recent option for adults and teenagers, clear aligners.
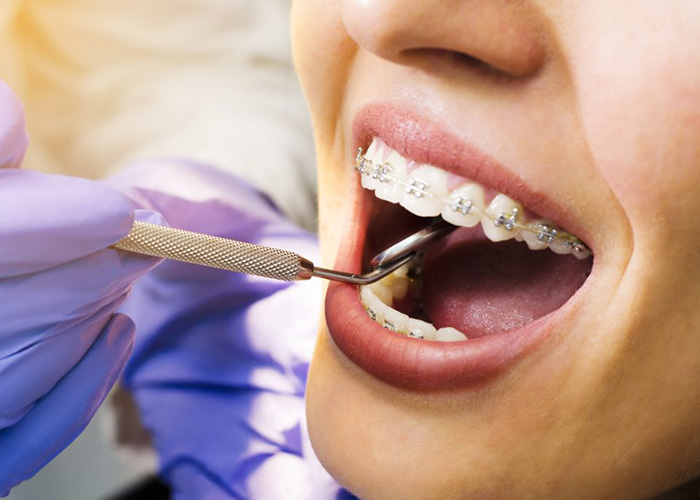
Spokane Valley's Top Orthodontic Treatment
Orthodontic treatment can alleviate a number of biting disorders that frequently start around the age of seven. When there is an underbite, a crossbite, or a significant overbite, the upper and lower teeth don’t close properly. Because there is still a space between the top and bottom teeth when the jaws are closed, crowding occurs when teeth are positioned either too closely or too widely apart.
Teeth must be shifted in order to rectify improper biting, but this is simpler than you might think! Teeth are held in place by the periodontal ligament, a tissue like a hammock that responds quickly to stresses applied to the teeth, rather than being set rigidly in their supporting bone. Orthodontic appliances work by exerting modest, consistent pressure while being kind to the teeth. Braces, which are made of metal wires that pass through tiny brackets connected to the teeth, or transparent aligners, which are made of semi-rigid plastic, may be used to provide this pressure.
Orthodontics is for Children and Adults
In order to take advantage of a child’s natural growth processes and assist in realigning their teeth, orthodontic therapy is best started when they are young. Teeth and jaws are growing swiftly, much like the rest of the body. Hence, it is already possible to extend the upper jaw swiftly with a “palatal expander” in order to provide the mouth more room for teeth. If more orthodontic appliances are required, this phase of growth modification can shorten overall treatment duration and produce the best results.
In order to benefit from a child’s natural growth processes and assist in moving teeth into optimal alignment, orthodontic therapy should begin in childhood. The teeth and jaws are undergoing fast transformation, just like the rest of the body. Currently, it is possible to quickly expand the upper jaw with a “palatal expander” to create more room for teeth, for example, in a crowded mouth. If additional orthodontic equipment is needed, this growth modification phase can help shorten overall treatment duration and produce the best results.
Types of Orthodontic Appliances
You frequently see tiny metal brackets that are affixed to the front of a person’s teeth and a thin wire that runs in between them when you think of someone wearing braces. Despite continued demand for the tried-and-true design, there are now more options. With the exception of the thin archwire, ceramic or plastic brackets used in clear braces are rarely noticeable. The only difference between lingual braces and traditional metal braces is that they are attached to the back of your teeth (on the tongue side), making them invisible.
Orthodontic hardware that is fixed can be replaced with removable clear aligners. They are made up of a set of properly shaped translucent plastic “trays” that gently shift your teeth into the proper position. Both permanent and movable equipment might have advantages and disadvantages depending on the circumstances. Your best treatment options will be discussed after a comprehensive evaluation.
Retention & Post Orthodontic Care
You must wear your retainer as instructed once your orthodontic treatment is finished. This is because teeth naturally wander back to their original positions after all of your hard work straightening them. Using a retainer helps keep your beautiful new smile looking great for the rest of your life by keeping your teeth in their new place for long enough for new bone and ligament to form around them.
Spokane Valley's Top Orthodontic Therapy - Orthodontist Near Me - Affordable Braces & Invisalign in Spokane Valley, WA
What do orthodontists do?
Orthodontists are dental specialists who diagnose and treat problems with the position, alignment or spacing of the teeth, and related irregularities in the face and the jaw. A number of special treatments, including braces and other oral appliances, are used to correct these problems.
Why should I (or my loved ones) get orthodontic treatment?
There are two good reasons: aesthetics and function. Having an attractive smile not only changes the way people see you — it enhances your own self-image as well. Orthodontic treatment also allows your teeth to function better and makes it easier to keep them clean, which can improve your overall health.
When should orthodontic treatment be started?
You’re never too old to begin orthodontic treatment — but if you start at an earlier age, your problems may be easier to treat. The American Association of Orthodontists recommends that a child who may need orthodontic treatment should come in for a first visit around age 7.
How can I recognize a potential bite problem?
Teeth that are protruding, crowded together or erupting out of position are clear indications that treatment is needed. Less obvious signs are mouth breathing, frequent biting of the cheek or palate, speech difficulties, and thumb sucking that goes past 3-4 years of age. If teeth don’t meet properly when the mouth closes, or if jaws make sounds or shift as they move, this may also indicate an orthodontic problem.
Does getting braces hurt? What about wearing them?
Having braces put on is generally painless. Some people experience minor aches and pains in the first couple of days or so, as they adjust to wearing their appliances; periodic adjustments may sometimes cause soreness as well, though it typically lasts only a short time. Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to alleviate any discomfort, but are usually unnecessary.
How long will treatment take?
It’s different for each person, but generally the active stage of treatment (that is, wearing braces or other appliances) may take from 6-30 months. After that, a retainer is worn for at least several months more.
How often will I come in for an appointment?
It depends on what’s being done, and how often you need to be monitored. During active treatment, you’ll typically visit the office once every 4 to 10 weeks.
Will I need to have any teeth extracted?
If your teeth are severely crowded (because your mouth is too small to properly accommodate all of them) — or if you have impacted teeth (teeth that are trapped beneath the gum line by other teeth) — then extraction may be necessary. In the case of younger patients, early treatment may make extraction unnecessary.
Will I have to watch what I eat?
Yes — you should pass up the types of foods that could damage or become trapped in your braces. Some of these include raw vegetables, hard candy, caramel, taffy and ice cubes (fortunately, ice cream is OK). You will receive a list of foods to avoid.
Will I be able to play sports/ play my instrument?
In a word: Yes. Of course, whether you wear braces or not, we recommend you wear a mouthguard when playing most sports. Musicians are generally able to play their instruments just as they did before, but they may need a short adjustment period after getting braces.
Do I still need to see my regular dentist while I’m getting orthodontic treatment?
You do — in fact, it’s more important than ever! Keeping teeth free of plaque (and potentially, decay) can be challenging when you’re wearing braces. Your dentist can help you avoid these problems with frequent cleanings and exams.
Will I wear a retainer when my braces come off?
Almost always, the answer is yes: If you don’t wear a retainer, your teeth can rapidly shift out of position — and then all the effort put into your treatment is lost! Your retainer helps you maintain that good-looking smile for a lifetime.
Is orthodontic care very expensive?
Orthodontic care is a long-term investment in your health and well-being. Yet its cost hasn’t increased as fast as many other consumer prices, and many financing options are available that make orthodontic care affordable. Weighed against the true cost of living with problem teeth, however, orthodontic treatment can be a wise investment indeed.
 One day in the not-too-distant future, your braces will come off. In a few moments, you’ll be free of bands and brackets, able to eat what you want and run your tongue over smooth, clean teeth. But, even on this happy occasion, please remember that you’re not quite done with orthodontic treatment yet: The next phase, called retention, is just beginning.
One day in the not-too-distant future, your braces will come off. In a few moments, you’ll be free of bands and brackets, able to eat what you want and run your tongue over smooth, clean teeth. But, even on this happy occasion, please remember that you’re not quite done with orthodontic treatment yet: The next phase, called retention, is just beginning.
Retention is a critical follow-through stage that typically involves wearing an orthodontic appliance called a retainer. Several different kinds of retainers are available, all of which are custom-made.
But if your teeth are straight now, why do you need a retainer at all? Simply put, it’s because if you don’t wear one, your teeth will start moving right back to where they were!
Teeth aren’t set rigidly in the jawbone — instead, they’re held in place by a network of fibers called the periodontal ligaments. After they have being moved, it takes several months for the periodontal ligament to adjust to the new position. So if you want to keep that new smile — and not waste all the time, effort, and money it took to get it — it’s essential to wear your retainer as directed.
Being fitted for a retainer usually happens on the same day your braces are removed. After your teeth are thoroughly cleaned, another set of X-rays and/or bite impressions may be taken to check how well your braces worked and to see how much your wisdom teeth have developed. Then, a retainer will be prepared for you.
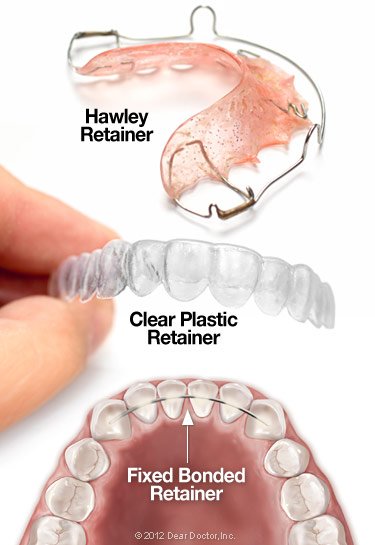
Three Types of Retainers
There are three basic types of retainers available today; each works best in particular situations. The most common is the so-called “Hawley” retainer — a thin, tongue-shaped piece of acrylic molded to fit your mouth, with a wire that holds your teeth in position. The Hawley retainer is simple, durable and easily removed. It’s even possible to personalize it by choosing different colors and designs for the plastic arch.
Finally, fixed retainers may be an option for some people, especially on the lower front teeth. As their name implies, they aren’t removable by the wearer — but they aren’t visible either. Like lingual braces, this system uses a wire which is bonded to the tongue side of the teeth. It may remain in place for months, or longer. This type of retainer is sometimes recommended when there’s a high risk that teeth could revert to their former position.
A Period of Adjustment
After a short time, most people adjust quite well to wearing a retainer. Some may find that they produce more saliva than usual for a day or so after first wearing any type of retainer — a normal reaction to a foreign object in the mouth. You may also find it a little harder to talk normally at first, but that problem will soon disappear. Of course, removable retainers should always be taken out when you eat or brush your teeth — a big change from braces!
At first, you will probably be told to wear your removable retainer all day, every day. This period of 24/7 retainer use generally lasts from several months to a year. Later, it may be OK to wear it only at night. Finally, you’ll probably need to put it on just a few nights a week.
Maintaining — and Retaining — Your Retainer
To stay fresh and germ-free, all retainers need proper cleaning. A Hawley-type retainer can be brushed gently with a regular toothbrush — but a brush may scratch the clear aligner types. Denture cleaners, in powder or tablet form, as well as special retainer cleaners, can be used to clean most removable retainers. Fixed retainers are cleaned by brushing and flossing; a floss threader or interproximal brush can also be a helpful cleaning tool when needed.
Finally, remember to always carry — and use — a retainer case. You’d be surprised how many retainers end up folded in a napkin and accidentally discarded! Also, don’t expose your retainer to excess heat by washing it in very hot water or leaving it on a heater: That can cause the retainer to warp and make it unusable. With proper care and conscientious use, a retainer can help you transition from braces to a permanent, healthy smile.
 You know how important it is to brush and floss properly when you’re wearing braces — but what’s the best way to do that? Let’s start with the basic brushing tools: Either a soft-bristle brush or a bi-level brush (one that has shorter bristles in the middle and longer bristles at the edges) can be effective. Used carefully, an electric toothbrush can work just as well. But be sure the electric brush is set to a moderate power level, and don’t let its vibrations cause the back of the brush to hit the braces!
You know how important it is to brush and floss properly when you’re wearing braces — but what’s the best way to do that? Let’s start with the basic brushing tools: Either a soft-bristle brush or a bi-level brush (one that has shorter bristles in the middle and longer bristles at the edges) can be effective. Used carefully, an electric toothbrush can work just as well. But be sure the electric brush is set to a moderate power level, and don’t let its vibrations cause the back of the brush to hit the braces!
You should brush with a fluoride toothpaste at least two times per day (preferably after meals), for at least two minutes each time. Remember to brush all of the tooth surfaces: the outside, the inside, and the chewing surfaces as well. Be especially careful to clean the areas between wires and teeth, and between brackets and gums — that’s where food particles can easily become trapped.
Here’s a suggested brushing technique: Beginning at the outside surfaces, place the tips of the bristles flat against your teeth, and use small circular motions to gently polish them clean. For areas between braces and gums, tilt the brush toward the gum line (down for the bottom teeth, up for the top) while keeping up the circular motions. Next, move on to the chewing surfaces of upper and lower teeth, using a firm back-and-forth motion. Finally, finish up by carefully brushing the inside surfaces of the teeth the same way you did the outside surfaces.
Special Brushing Tools
If you’re having trouble cleaning the areas near brackets and wires, there are some special tools that may help. One is the interdental toothbrush, or proxabrush. It has a small tuft of bristles that stick up all around, like a pipe cleaner. Use it gently and carefully to clean the tiny spaces under wires and around bands and brackets.
Another special cleaning tool is the oral irrigator or “water pick.” This device shoots a small stream of pressurized water at your teeth, which can help dislodge bits of food that become trapped in nooks and crannies. While it’s easy to use, an oral irrigator isn’t a substitute for a toothbrush or dental floss — but when used along with proper brushing and flossing techniques, it can be very effective.
Floss Fundamentals
To keep your teeth and gums clean and healthy, you need to floss at least once per day. But how do you get floss under the archwire of your braces? It’s not so hard with the help of a floss threader. Using this device is somewhat like threading a needle: You pull one end of floss through the threader, and then push the threader — carrying with it the free end of the floss — under the archwire. Now grasp the floss on each end and slide it up and down the sides of both teeth, and all the way under the gums until you hear a squeaky sound. Finally, pull it out and use a new section of floss for the next area.
Full Disclosure
Ever wonder how effective your tooth-cleaning techniques really are? There’s an accurate way to tell, using special vegetable dyes called “disclosing solutions” or “disclosing tablets.” As they dissolve in the mouth, these dyes highlight plaque and food debris that brushing has missed. You can then easily remove the dyed spots — and you’ll know for sure if your oral hygiene methods need a little “brushing up.”
Keeping your teeth and gums healthy now is an investment in your future. It enables you to get the best results from your orthodontic treatment, and starts you toward a brighter smile that can last for a lifetime.
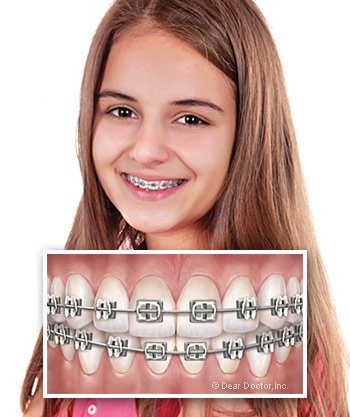
 There are more and more adult orthodontic patients these days, and it’s not hard to figure out why. Appliances that are barely noticeable have been developed to give adults more discreet choices when it comes to orthodontic treatment. And many adults realize that investing in a smile makeover can have significant benefits, socially and professionally. Straightening teeth can be an important part of that confidence-boosting makeover process.
There are more and more adult orthodontic patients these days, and it’s not hard to figure out why. Appliances that are barely noticeable have been developed to give adults more discreet choices when it comes to orthodontic treatment. And many adults realize that investing in a smile makeover can have significant benefits, socially and professionally. Straightening teeth can be an important part of that confidence-boosting makeover process.
Healthy teeth can be moved at any age, so there’s no such thing as being too old for braces. However, orthodontic treatment for adults is different in two important respects: For one thing, the growth and development of the jaws is complete in adults, so changes in actual jaw structure can’t be accomplished with orthodontic appliances in the way they can with a growing child.
Secondly, periodontal (gum) disease is more prevalent in adults than in children. While you are wearing the orthodontic appliances, gentle forces will be applied to your teeth so they can move through their surrounding bone. Periodontal health plays a key role in all of this; if the gum tissues are not healthy during orthodontics, bone loss can result and weaken the long-term prognosis of your teeth. So any gum disease must be brought under control before orthodontic treatment begins. And to maintain your periodontal health, you will need to make sure to have regular professional cleanings during the orthodontics while maintaining good oral hygiene at home.
Types of Orthodontic Appliances
All orthodontic appliances work essentially the same way: by employing light, constant force to move teeth into proper alignment. But how we apply these forces can vary, as numerous innovations have become available in recent years. Some of the newer, less visible orthodontic appliances have been designed to blend more easily into an adult’s personal and professional lifestyle. Types of orthodontic appliances include:
Traditional Metal Braces — This is probably what you think of when you picture someone wearing braces: small metal brackets bonded to the front of the teeth. A thin wire runs through the brackets and is attached on either end to metal bands that go around a back molar.
Clear Braces — Instead of highly noticeable metal brackets, you can have clear ones made of ceramic, plastic or a combination of both. They are hardly visible, except for the thin wire running through, but they are more susceptible to breakage than metal braces.
Clear Aligners — As an alternative to the fixed type of orthodontic appliances mentioned above, clear aligners are removable. They are actually a series of clear plastic “trays” that fit over your teeth exactly. Each tray is part of a series of trays that move your teeth a little bit at a time until they are in the proper position. Your trays are designed with the help of specialized computer software that generates a virtual model of your bite.
Lingual Braces — These metal braces are bonded to the back of your teeth (tongue side) so that no one can see them. That is the plus side. On the minus side, they can be more difficult to get used to wearing, and are more expensive than traditional braces.
After Treatment
Wearing a retainer after orthodontic treatment is crucial, no matter which type of appliance you choose and what age you happen to be. Teeth that are not held in place by a retainer long enough for new supporting bone to develop around them can drift back to their original positions, and that’s certainly not something you want to see happen. You will be instructed on how to retain your new, more beautiful smile so that it continues to make you look and feel great for years to come.
 Your first appointment is an exciting time! It’s a chance for you to learn about the treatments and services that can help give you the best smile possible. It all starts with the initial consultation.
Your first appointment is an exciting time! It’s a chance for you to learn about the treatments and services that can help give you the best smile possible. It all starts with the initial consultation.
You should plan to spend at least an hour at the first visit. That’s to ensure that no one has to rush, and that you get plenty of time to ask any questions you may have. You will meet one of the receptionists or patient coordinators, who will take some information from you and bring you through the office. Then it’s time for some diagnostic work and an exam.
Making a Plan
A big part of the first visit is to determine what treatment is necessary to correct any problems found — and whether to begin now, or wait until a later time. The procedure starts by taking a set of regular photographs of the teeth in their present state. Next, a series of radiographic (X-ray) images will be taken. These show what’s going on underneath the gums: the position and growth of bones and joints, and the teeth that are still below the gum line.
In some cases, an impression (mold) of the teeth is also taken to create an exact replica of the bite. This helps reveal exactly what the problem is and how best to treat it. The impression is made by biting down on some soft putty-like material for a few moments; then it’s removed.
After that, it’s time for the exam. Besides looking in the mouth, we you may be asked questions, such as whether the jaws make noise when the mouth is opening or closing, or if there are any problems chewing or swallowing. Taken together, this information will yield a proper diagnosis so a treatment plan can be finalized at the first visit.
Discussing Your Treatment Options
Following the exam, you may be told that things are just fine — or, treatment may be recommended. It might begin right away or at a later time, depending on the developmental stage of the teeth and jaws. Many times, you’ll be advised to return for periodic checkups until it’s time to start.
Whether you’re starting now or later, the first visit is the best time to ask questions about the process. Topics to discuss include treatment choices, what to expect at the different stages of the process, and any of the following:
- Can orthodontic treatment benefit me (or my child)?
- What general procedures will be used to correct the problem?
- Are any options available (or recommended) for my treatment?
- Should I get treatment now, or is it better to wait?
- Will tooth extraction be necessary?
- How much does treatment cost? Are payment plans available?
- How long do you expect treatment should take?
When you leave the office, you should have a better understanding of how you can get the best possible smile.
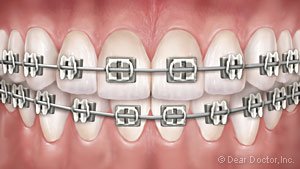
 For the vast majority of orthodontic patients, wearing fixed appliances (commonly called braces) will be a major part of treatment — and those braces, for the most part, will be the familiar silvery-metal type. But while they’re still quite popular, traditional-looking metal braces are no longer the only game in town! Let’s have a look at some of the options available in orthodontic appliances.
For the vast majority of orthodontic patients, wearing fixed appliances (commonly called braces) will be a major part of treatment — and those braces, for the most part, will be the familiar silvery-metal type. But while they’re still quite popular, traditional-looking metal braces are no longer the only game in town! Let’s have a look at some of the options available in orthodontic appliances.
First, we should distinguish between fixed and removable appliances. Fixed appliances like braces are attached to the teeth by metal bands or special cement. They aren’t normally taken off until treatment is complete. Removable appliances, such as clear aligners, are typically worn some 22 hours per day, but may be easily taken off as needed. While clear aligners can be effective in treating mild to moderate orthodontic problems, fixed appliances are generally needed for more comprehensive treatment.
Metal Braces
Typically made of high-grade stainless steel, traditional metal braces remain by far the most common type of fixed orthodontic appliances. They consist of metal bands that wrap around the molars in back, and smaller metal brackets that are cemented to the front surfaces of the other teeth. A thin, springy metal wire, running through the brackets, gently guides the teeth into a proper position. This archwire may be fixed to the brackets by flexible elastics, metal ties, or other types of clasps.
There are many good reasons why time-tested metal braces remain popular — because they offer a reliable, effective and economical treatment option. In contrast to the appliances of the past, today’s braces are actually smaller, lighter, and more comfortable to wear. If you want a less traditional look, you may be able to choose colorful elastics for the brackets, or other modifications.
Ceramic braces
Clear ceramic braces are a new variation on the traditional system that provides a far less noticeable method of treatment. They use the same components as traditional braces — except that the brackets on the front side of the teeth are made of a translucent ceramic material that blends in with the tooth’s natural color. This system has become a favorite for adults (including some well-known celebrities) because, unless you look closely, it’s hard to notice they’re there.
Several types of ceramic braces are currently available, and the technology is constantly improving. Their aesthetic appeal is undeniable… but there are a few tradeoffs. The ceramic brackets can be less durable than their metal counterparts; plus, while the brackets themselves don’t stain, the elastic bands that attach them to the archwire do (however, these are generally changed each month.) Ceramic braces also cost more than metal — but for many people, the benefit of having an inconspicuous appliance outweighs the costs.
Lingual Braces
While ceramic braces certainly offer a less conspicuous look, there is still another system that allows fixed braces to be truly invisible. In some situations, special appliances called lingual braces can be placed on the tongue side of the teeth. They work the same way other metal braces do — but even though they’re made of metal, they can’t be seen, because they’re hidden behind the teeth themselves!
Lingual braces aren’t the proper treatment for every orthodontic condition. Special training is required to install them, and they’re significantly more expensive than standard braces. They also generally require a bit more time for the wearer to get used to them, and they may slightly prolong treatment. But if you want the least visible type of fixed appliance — and if you’re a candidate for this treatment option — then lingual braces may be just what you’re looking for.
 At first, having orthodontic treatment may take a little getting used to. It isn’t uncommon to experience a bit of soreness when appliances are first put on, or some minor aches as teeth begin moving into new positions. Yet it’s comforting to know that genuine orthodontic emergencies are rare.
At first, having orthodontic treatment may take a little getting used to. It isn’t uncommon to experience a bit of soreness when appliances are first put on, or some minor aches as teeth begin moving into new positions. Yet it’s comforting to know that genuine orthodontic emergencies are rare.
If you think you may have an emergency, however, the first step is to determine the severity of the problem: Is it an urgent situation that requires immediate attention, or a minor problem that you can take care of yourself, temporarily, until you can come in to the office?
A Major Emergency
There are only a few true orthodontic (or dental) emergencies. They include:
- Trauma or injury to the teeth, face or mouth
- Infection or swelling of the gums, mouth or face
- Severe, unmanageable discomfort or pain in these areas
In any of these situations, you should seek help as soon as possible — go to an emergency room, if that’s your best option. Generally, however, the place to start is at the dental office. If, for example, you have a fractured tooth, that immediate problem requires diagnosis and treatment. Afterwards your orthodontic treatment plan can be adjusted as needed. Likewise, severe pain or swelling could be a sign of infection or disease, which also needs immediate treatment.
Some Minor Troubles
Fortunately, the vast majority of orthodontic problems are minor compared to these situations — but they may still cause discomfort or irritation. In general, it’s best to try and soothe the immediate cause of the discomfort, and then call for an appointment. Here are a few of the more common orthodontic problems, along with some tips on what you can do to relieve them at home:
Loose or broken brackets, bands or wires
This problem is often caused by eating hard or sticky candy or food, or playing with the braces. If the band or bracket is still attached to the wire, leave it as is — but don’t connect any elastics to it! You can cover it with orthodontic wax if it’s irritating the inside of your mouth. If it has come off, save it. In either case, call our office to let us know what happened, and we will recommend the next step.
Misplaced or poking archwire, bracket or tie
As the teeth start to move, the wire that connects them (archwire) may begin poking near the back of the mouth or irritating the cheeks. You can try moving the wire into a better position with a pencil eraser or a Q-Tip. If the wire won’t move, you may be able to cut the end off with a nail clipper sterilized in alcohol — but before doing so, please call for guidance or instructions. Often, you can also use tweezers to gently move a misplaced wire or a tie that’s causing problems.
When wires or brackets cause irritation, covering the metal parts with wax will often help ease the discomfort. As with any of these types of problems, it’s best to make an appointment so it can be taken care of.
General tooth pain or loosening
It’s normal for teeth to become slightly loosened during orthodontic treatment — that shows they’re moving! Sometimes, this movement may be accompanied by tenderness, especially after braces are placed or adjusted. For minor soreness, you can use your regular over-the-counter pain reliever. A twice-a-day salt-water rinse may also help: Mix one teaspoon of salt in an 8-ounce glass of warm water, and rinse for 30 seconds. A warm washcloth or heating pad placed on the outside of the jaw can also offer some relief.
While actual emergencies are rare, the goal is to make orthodontic treatment as comfortable as possible.
 Is there any image that illustrates the comforts of babyhood better than a sleepy infant sucking his or her thumb? Ultrasound pictures have shown, to the joy of many prospective parents, that this behavior can even occur in the womb. The thumb- or finger-sucking habit seems to relax and comfort toddlers too, and it’s perfectly natural. But as a child grows, there comes a point where this habit isn’t just socially awkward — it may also be harmful to his or her oral health.
Is there any image that illustrates the comforts of babyhood better than a sleepy infant sucking his or her thumb? Ultrasound pictures have shown, to the joy of many prospective parents, that this behavior can even occur in the womb. The thumb- or finger-sucking habit seems to relax and comfort toddlers too, and it’s perfectly natural. But as a child grows, there comes a point where this habit isn’t just socially awkward — it may also be harmful to his or her oral health.
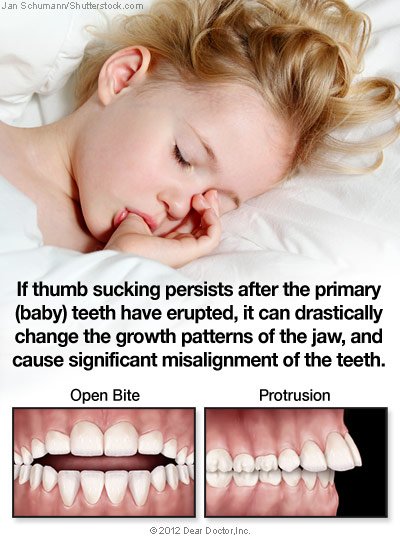
In most children, thumb sucking stops on its own between the ages of two and four years. But if the practice persists after the primary (baby) teeth have erupted, it can drastically change the growth patterns of the jaw, and cause significant misalignment of the teeth. It may be hard to believe that such a benign habit can actually move teeth and bone — but there are a number of reasons why this occurs.
Children’s jaws, rich in blood supply and growing rapidly, are relatively soft and flexible — especially in kids under the age of 8. So it really isn’t hard for the constant pressure of a thumb or finger to deform the soft bone around the upper and lower front teeth. Children who are particularly vigorous thumb suckers are even more likely to change the growth patterns of the teeth and jaws.
If the thumb sucking habit persists, it can result in the upper front teeth flaring out and the lower ones moving back and inward. It can also hold back the growth of the lower jaw, while causing the upper jaw to be thrust forward. This can result in misalignment of the teeth, an anterior open bite (where the front teeth fail to close together), collapse of the upper jaw causing crossbite, or other problems. That’s why it is important to stop the behavior at an appropriate time, before damage occurs.
Controlling Thumb or Finger Sucking
Like many potentially harmful behavior patterns, thumb sucking can be a difficult habit to break. Through the years, parents have tried a variety of home remedies, such as having the child wear gloves, coating the digits with a bitter-tasting substance — and even reasoning with their toddlers. Sometimes it works — but in other cases, the allure of thumb sucking proves very difficult to control.
If your child has a thumb or finger sucking habit that has persisted past the age of 3, and you’ve been unable to tame it, then it may be time for you to visit the dental office for a consultation. A “habit appliance” such as a fixed palatal crib or a removable device may be recommended for your child. This crib isn’t for sleeping — it’s a small metal appliance worn inside the mouth, attached to the upper teeth.
How does it work? The semicircular wires of a palatal crib keep the thumb or finger from touching the gums behind the front teeth. Simply preventing this contact seems to take all the enjoyment away from the thumb sucking habit — and without that pleasurable feedback, a child has no reason to continue the behavior. In fact, the device is often successful the first day it’s worn.
Getting and Using a Habit Appliance
If your child could benefit from a habit appliance, the first step is to get a thorough examination, which may include taking x-rays, photographs and dental impressions. If it’s recommended, a crib will then be custom-fabricated to fit your child’s mouth, and placed at a subsequent appointment. Afterwards, your child will be periodically monitored until the appliance is removed — typically, a period of months.
Although wearing the crib isn’t painful, your child may experience some soreness in the upper back teeth for a few hours after it’s first installed. He or she may also have a little trouble falling asleep for a day or two afterward. Plenty of extra attention and TLC are usually all that’s needed to make everything all right. While the appliance is being worn, it’s best to avoid chewing gum and eating hard, sticky food that might cause it to come loose.
A Word About Tongue Thrusting
Like thumb sucking, tongue thrusting is a normal behavioral pattern in young children. It’s actually part of the natural infantile swallowing pattern, which will normally change on its own — by the age of six, in most children. If the pattern doesn’t change, however, it can lead to problems similar to those caused by thumb sucking: namely, problems with tooth alignment and skeletal development. Fortunately, this problem can be successfully treated with a habit appliance that’s very similar to a fixed palatal crib.
 Every so often, in dentistry and other fields, a new technology comes along that promises to change the standard practices. TADS (Temporary Anchorage Devices) aren’t exactly new — orthodontists have used them since the 1980s — but they’re gaining widespread acceptance today. The benefits they offer some orthodontic patients could even be called groundbreaking. Let’s look at what these devices are, and what they can do.
Every so often, in dentistry and other fields, a new technology comes along that promises to change the standard practices. TADS (Temporary Anchorage Devices) aren’t exactly new — orthodontists have used them since the 1980s — but they’re gaining widespread acceptance today. The benefits they offer some orthodontic patients could even be called groundbreaking. Let’s look at what these devices are, and what they can do.
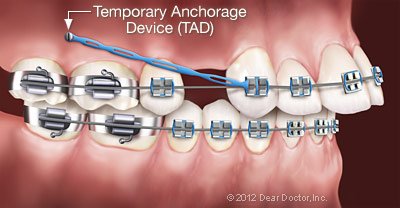
Essentially, TADS are small, screw-like dental implants made of a titanium alloy. As the name implies, they’re temporary — they usually remain in place during some months of treatment, and then they are removed. Their function is to provide a stable anchorage — that is, a fixed point around which other things (namely, teeth) can be moved. But why is anchorage so important?
Moving teeth in the jaw has been compared to moving a stick through the sand. With the application of force, sand moves aside in front of the stick, and fills up the space behind. The “sand” in this case consists of bone cells and cells of the periodontal ligament, which attaches the tooth to the bone. These tissues slowly move aside and reform as force is applied to them by orthodontic appliances, such as wires and elastics.
But to do its work, that force needs a fixed point to push against. For example, imagine trying to move the stick while you’re floating free in the water: Not so easy! But with two feet firmly planted in the sand, you can do it. When possible, orthodontists use the back teeth as an anchor — but sometimes, cumbersome headgear may be required to provide the necessary anchorage. In many cases, using TADS can change that.
What TADS Can Do
While it’s generally preferred, the use of teeth as orthodontic anchors can have drawbacks in some cases. For example, there may not be a viable tooth located at the point where an anchor is needed. Also, when a greater force is required, the teeth used as anchors can themselves start to move. This is one instance where TADS are beneficial: These mini-implants can eliminate the need to use teeth as anchors, or stabilize a tooth that’s being used as such.
TADS can also provide an anchorage point for a pushing or pulling force that would otherwise need to be applied from outside the mouth: generally, via orthodontic headgear. Wearing headgear can be uncomfortable, and compliance is sometimes a problem. In many situations TADS can eliminate the need for headgear, a welcome development for many patients.
The use of TADS offers other benefits as well: It may shorten overall treatment time, eliminate the need to wear elastics (rubber bands) — and in some cases, even make certain oral surgeries unnecessary. It also allows orthodontists to take on complex cases, which might formerly have proved very difficult to treat. This small device can really do a big job!
Getting (and Maintaining) TADS
Like dental implants (which have been in use since the 1970s) TADS are small, screw-like devices that are placed into the bone of the jaw. Unlike implants, however, they don’t always need to become integrated with the bone itself: They can be fixed in place by mechanical forces alone. Plus, they’re much easier to put in and remove when treatment is complete. How easy?
Placing and removing TADS is a minimally-invasive, pain-free procedure. After the area being treated is numbed (with an injection or other numbing treatment), a patient feels only gentle pressure as the device is inserted. The whole process can take just minutes to complete. Afterwards, an over-the-counter pain reliever can be taken if needed — but many patients need no pain reliever at all. And taking TADS out is even easier. So if you’re worried that it may be a painful procedure: Relax! It’s far less stressful than you may think.
While they’re in place, TADS require minimal maintenance. Generally, they should be brushed twice daily with a soft toothbrush dipped in an antimicrobial solution. You will receive specific instructions regarding maintenance when your TADS are placed.
Not every orthodontic patient needs TADS — but for those who do, it’s a treatment option that offers some clear benefits.
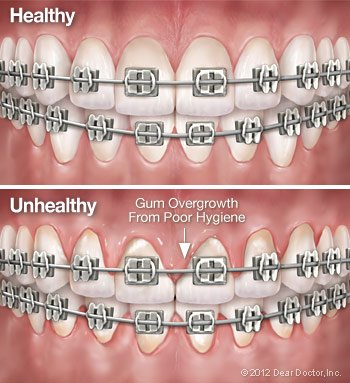 You already know that maintaining good oral hygiene is important for everyone — but when you’re having orthodontic treatment, it’s even more critical. Why? Because, while the appliances (such as braces or clear aligners) you may need to wear during treatment are very effective in correcting misaligned teeth, they can also trap food particles easily. Keeping your teeth (and your appliances) clean is a little harder — but you can do it! Here’s a look at why good oral hygiene is so important during orthodontic treatment, and some tips on how you can keep it up.
You already know that maintaining good oral hygiene is important for everyone — but when you’re having orthodontic treatment, it’s even more critical. Why? Because, while the appliances (such as braces or clear aligners) you may need to wear during treatment are very effective in correcting misaligned teeth, they can also trap food particles easily. Keeping your teeth (and your appliances) clean is a little harder — but you can do it! Here’s a look at why good oral hygiene is so important during orthodontic treatment, and some tips on how you can keep it up.
The major enemy of oral health is plaque. Food that becomes trapped near tooth surfaces can lead to the formation of plaque — a thin coating of microorganisms and organic debris (biofilm) containing potentially harmful bacteria. Braces or other appliances make it harder to remove plaque. The bacteria in plaque digest the sugars in food, producing acids which may erode teeth and irritate gums. This can cause cavities, white spots on teeth, gum disease and bad breath.
Keeping plaque under control is one of the most effective means of maintaining strong, healthy teeth and gums. There are three general ways to do it: through diet, daily maintenance, and regular professional care. Taken all together, they’re your teeth’s best defense.
Diet and Decay
Controlling your diet involves avoiding foods that could increase your risk of developing tooth decay. That means cutting down or eliminating foods with an excess of sugar, like soda, sweets, and ice cream. It also means avoiding foods that could easily become stuck in your braces, like toffee, gum, licorice and caramels.
Foods that are very hard or extremely sticky can also cause physical damage to orthodontic appliances. Certainly braces or retainers with broken wires or loose brackets aren’t working to straighten your teeth! You should avoid foods like hard candies or nuts, beef jerky and hard pizza crust. Keep eating healthy foods like carrots and apples — but cut them into bite-sized pieces first! And don’t chew on ice, pencils, or your nails: these habits can cause damage to your appliances, and even result in chipped teeth!
Daily Maintenance
You know how important brushing and flossing are for keeping a healthy smile — especially now that you’re in orthodontic treatment. But sometimes it’s harder to clean your teeth effectively around an appliance’s brackets and wires. Here are some tools and tips you can try for better tooth cleaning.
Either a soft-bristle or a bi-level toothbrush (one with longer bristles on the edges and shorter ones in the middle) can be effective in plaque removal — even with braces. An electric toothbrush can also be used, on a moderate setting. For hard-to-clean areas, try an interdental brush, or proxabrush. The small bristles of this special tooth-cleaning aid, which is shaped like a pipe cleaner, can get in between wires, brackets and teeth. With gentle and persistent effort, it’s possible to reach into the smallest nooks and crannies, and control plaque buildup.
You should floss at least once a day during orthodontic treatment. While it’s a little harder to do with braces, there are some special products available — including floss threaders and particular kinds of floss — that can help you get the floss between wires and gum line. The office staff will review proper brushing and flossing techniques with you when your braces are put on — but if you ever have questions, don’t hesitate to ask!
Depending on your situation, an in-office or at-home supplemental fluoride treatment may be recommended to boost your cavity resistance. An antiseptic rinse may also be recommended, to ease minor gum inflammation or irritation.
If you have a retainer, it should be brushed daily, the same way you brush your teeth. A cleaning solution may be recommended — but never put hot water on your retainer, because it can distort the soft plastic and make it unusable! And always keep it in a case when it’s not in your mouth.
Professional Care
During orthodontic treatment, it’s as important as ever to make sure your teeth stay healthy with thorough examinations, cleanings and preventive care. Your orthodontic treatment is a team effort where everyone has an important role to play. And the team has just one goal: giving you a winning smile.
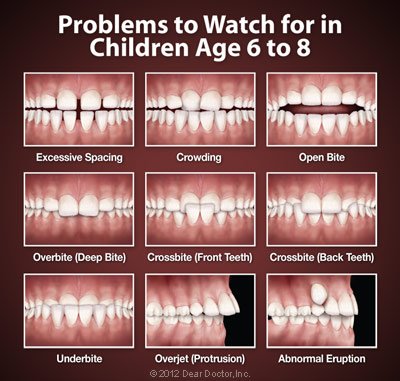 You probably know that it’s never too late to begin orthodontic treatment — but when it comes to your youngster’s teeth, did you know that earlier may be better than later? According to the American Association of Orthodontists, kids should have an initial orthodontic screening at age 7. What makes early evaluation — and potentially, early treatment — so important?
You probably know that it’s never too late to begin orthodontic treatment — but when it comes to your youngster’s teeth, did you know that earlier may be better than later? According to the American Association of Orthodontists, kids should have an initial orthodontic screening at age 7. What makes early evaluation — and potentially, early treatment — so important?
There are several ways that kids can benefit from an orthodontic evaluation at an early age. But it’s important to recognize that early evaluation isn’t necessarily followed by early treatment; in most cases, if orthodontic work is needed, your child’s growth patterns are simply monitored until it’s time for treatment to begin. This creates an opportunity to get the best results in the most efficient way, and to help prevent future problems.
Although every child’s development is different, in most kids the first adult molars have typically started to emerge by around age six. At this point it is possible to evaluate the basic alignment of the teeth, from front to back and side to side. It may also be possible at this point to determine whether there is adequate room in the mouth for all of the permanent teeth — and, if not, to take action.
When Earlier Treatment Is Better
Treatment for common orthodontic problems typically begins around age 9-14, when all of the baby teeth are gone and many of the permanent ones are in place. But there are some conditions that are much easier to treat if they’re caught at an early age, when a child’s natural growth processes are going full speed ahead.
One is severe crossbite, a condition where the upper teeth close inside the lower teeth. To treat this problem, a device called a palatal expander can be used, which gradually and painlessly widens the upper jaw; it’s especially effective when the jaw itself hasn’t fully developed. If one waits too long, a more complicated treatment — or even oral surgery — might be required to correct the problem.
Another condition that may benefit from early treatment is severe crowding. This occurs when the jaws are too small to accommodate all of the permanent teeth. Either palatal expansion or tooth extraction may be recommended at this point, to help the adult teeth erupt (emerge from below the gums) properly. Even if braces are required later, the treatment time will likely be shorter and less complicated.
Early intervention may also be helpful in resolving several other problems. Protruding teeth, especially in front, can be prone to chipping and fractures; they may also lead to problems with a child’s self-image. A severe underbite, caused by the lower jaw growing much larger than the upper jaw, can result in serious bite problems. Orthodontic appliances, including braces and headgear, can be successfully used to correct these problems at this stage, when the child’s development is in full swing, thereby increasing the chances that surgery can be avoided.
Correcting Bad Habits
At one time or another, anyone may pick up a bad habit. But there are some situations where a youngster’s parafunctional (detrimental to health) habits can actually influence the development and function of his or her teeth, jaws and mouth. Some examples of these are persistent thumb sucking, tongue thrusting and mouth breathing.
The sucking reflex is natural in early childhood; it usually disappears between ages 2 and 4. But if it persists much later, the pressure of the digit on the front teeth and the upper jaw can actually cause the teeth to move apart and the jaws to change shape. This can lead to the orthodontic problem called “open bite,” and may impair speech. An open bite can also be caused by the force of the tongue pushing forward against the teeth (tongue thrusting).
Mouth breathing — an abnormal breathing pattern in which the mouth always remains open, passing air directly to the lungs — is related to alterations in the muscular function of the tongue and face. It may cause the upper and lower jaw to grow abnormally, which can lead to serious orthodontic problems. Although mouth breathing may start from a physical difficulty, it can become a habitual action that’s hard to break.
Various orthodontic treatments are available to help correct these parafunctional habits — and the sooner they’re taken care of, the less damage they may cause. But these potential problems aren’t always easy to recognize. That’s one more reason why you should schedule an early orthodontic screening for your child.
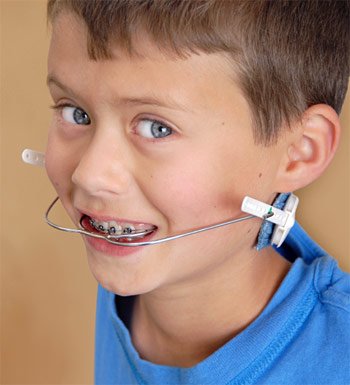 Sometimes, braces alone aren’t enough to move teeth into a better position, or to correct trouble with the bite or remedy problems in the growth of the jaws. In those situations, special appliances may be recommended. Orthodontic headgear is the general name for an appliance, worn partly outside the mouth, which creates just enough force to move the teeth properly and guide the growth of the face and jaws.
Sometimes, braces alone aren’t enough to move teeth into a better position, or to correct trouble with the bite or remedy problems in the growth of the jaws. In those situations, special appliances may be recommended. Orthodontic headgear is the general name for an appliance, worn partly outside the mouth, which creates just enough force to move the teeth properly and guide the growth of the face and jaws.
There are several different types of orthodontic headgear, each designed to work best in a specific situation. A treatment program will be designed to address your individual needs, and select the most appropriate type of headgear; you will also be instructed on its use and care. It’s important for you to follow instructions carefully so that you can achieve the best results from your treatment.
Types of Headgear
One common type of headgear is called the cervical pull type. This appliance has a U- shaped wire that attaches to the bands on your back teeth, and a strap that is worn behind your neck. A similar device is the high-pull headgear, which also has a wire connecting to the teeth, plus a strap that goes behind and over the head.
These types of headgear are typically used to correct an excessive horizontal overbite (technically called an “overjet”) in children, by holding back the growth of the upper jaw. They can also be used for adults who need help maintaining a proper bite and correct tooth spacing after tooth extraction. Generally, these types of headgear are designed to be worn from 12-14 hours each day.
Another type of headgear is the reverse-pull or “facemask” type. This appliance is generally used to correct an underbite. It gently pulls the upper jaw forward (instead of back), which allows it to catch up with the lower jaw. It consists of two pads — one resting on the forehead, the other on the chin — connected by a vertical frame. Elastics or wires, which connect from the frame to the braces, exert the pulling force. It may be necessary to wear this appliance from 14-16 hours daily.
Making Headgear Work Depends on You
Whichever type of headgear you’re wearing, there are some important things you should know. Probably the most essential one is this: In order for it to be effective, you must carefully follow instructions about wearing your headgear — that means putting it on each day for the time specified. If you wear headgear at night and you miss one night, you must make up the time the following day — otherwise, everything you’ve accomplished in the previous seven days of wear could be wiped out!
It’s normal to feel some discomfort as you get used to wearing orthodontic headgear. Fortunately, if you wear it faithfully, the discomfort generally goes away in a few days. An over-the-counter pain reliever like Ibuprofen, and/or a soft diet, may be recommended to help you adjust.
From time to time you may also experience some soreness when chewing, or even a little looseness in the first molars. This is normal, and it shows the appliance is working. However, if you have unusual pain, notice that the anchor band on your first molar (the one the headgear attaches to) has come loose, or find that the headgear suddenly seems not to fit correctly, it could signal a problem that requires immediate attention.
Maintain Your Headgear — And Your Oral Health
To keep your orthodontic headgear working as it should — and to maintain your overall oral health — it’s important that you follow all instructions about care and cleaning. It’s also important that you learn to put headgear on and take it off properly and safely. Remember to bring it with you every time you have an orthodontic appointment — but leave it behind when you’re playing sports, or even horsing around in the living room!
Wearing orthodontic headgear may seem like a big adjustment — and nobody would deny that it takes some getting used to. When everyone works together, it’s possible to achieve your goal: a beautiful smile that you’ll have for your whole lifetime.
 For many teens, braces are a rite of passage: They’re one more example of the changes adolescents go through at this time — along with growth in stature, edgier tastes in clothes and music, and an increasing degree of self-awareness. But is there any particular reason why orthodontic appliances and teenagers seem to go together? In a word: Yes.
For many teens, braces are a rite of passage: They’re one more example of the changes adolescents go through at this time — along with growth in stature, edgier tastes in clothes and music, and an increasing degree of self-awareness. But is there any particular reason why orthodontic appliances and teenagers seem to go together? In a word: Yes.
There are several good reasons why adolescence is the optimal time for orthodontic treatment, though occasionally even earlier intervention is called for. One has to do with the development of the teeth: There’s no set timetable for every kid, but generally by the age of 11-13 the deciduous (baby) teeth have all been lost, and the permanent ones have largely come in. This is the time when we can go to work correcting the problems that cause a bad bite (malocclusion), improper tooth spacing or poor alignment.
Orthodontic problems don’t improve with age — they simply become harder to treat. It’s easier to treat many orthodontic problems during adolescence because the body is still growing rapidly at this time. Whether standard braces are used, or appliances like palatal expanders, improved appearance and function can be created in a short period of time. In later years, when the bones of the face and jaw are fully developed, many conditions become more difficult (and costly) to treat.
There’s even a social element to getting orthodontic treatment in adolescence. If you need braces, you’re not alone! Chances are you’ll see some of your classmates in the dental office, and you may even make new friends as you go through the process together. When it’s done, you’ll have a smile that you can really be proud of, and benefits that will last your whole life.
The Orthodontic Treatment Process
What can you expect when you have orthodontic treatment? It all depends on what kind of treatment you need. At your first appointment, pictures and radiographic (X-ray) images of your mouth are usually taken, along with impressions of your teeth, so that a model of your bite can be made. This information will be used to develop a treatment plan. It may involve regular braces, with or without elastics (rubber bands). A specialized appliance may also be recommended for a period of time. Here are some of the most commonly used orthodontic appliances:
Metal Braces need no introduction. But you might be surprised to find they’re smaller and lighter than ever. They may even offer some customized options, like colored elastic ties on the brackets.
Clear Braces feature brackets made of ceramic or composite materials which blend in with your teeth, making them harder to notice. They’re suitable in many situations, but they cost a little more.
Clear Aligners for teens is a series of removable, clear plastic trays that gradually straighten teeth as they’re worn (for 22 hours per day). Formerly recommended only for adult patients, they now come with special features — like compliance indicators to tell how often you’ve been wearing them — that make them appropriate for teens in some situations. The advantage: they’re practically invisible!
Lingual Braces offer the most unnoticeable form of orthodontic treatment because they are attached to the back (tongue side) of the teeth, where they cannot be seen at all.
Other orthodontic appliances may be recommended in some cases, where major tooth or jaw movement is needed. They can range from small devices that fit inside the mouth to external headgear. But don’t worry: You’ll get used to them, and they’re temporary — but they provide a long-term benefit in a short time.
How Long Will I Wear Them?
There’s no one answer that fits everyone: It all depends on what has to be done in your individual situation. Generally, however, the active stage of orthodontic treatment lasts 6-30 months. Afterwards, you will wear a retainer for another period of months. When your orthodontic treatment is complete, a new smile will be yours for a lifetime.
Meet Your Top-Rated Family Dentist in Spokane Valley

Our Dental Services
Dental Crowns
Emergency Care
General Dentistry
Implant Dentistry
Orthodontics
Pediatric Dentistry
The Proof is in our Patients